
Celebrate Everyday Wins
DIACOMIT® can help patients with Dravet syndrome achieve seizure freedom.1-3
So, families like yours can spend less time battling seizures and more time celebrating everyday wins.
DIACOMIT is an FDA-approved antiseizure medication developed specifically to treat seizures associated with Dravet syndrome in children 6 months and older (weighing 15 lb or more) taking clobazam.1
Some common side effects included sleepiness, decreased appetite or weight, and agitation.1
Trust in Proven Experience
Biocodex, a pioneer in Dravet syndrome treatment, develops stiripentol
FDA approves stiripentol for compassionate use in the United States
DIACOMIT is approved in the European Union
Stiripentol is officially FDA approved and now known as DIACOMIT®
FDA expands the indication to include patients as young as 6 months
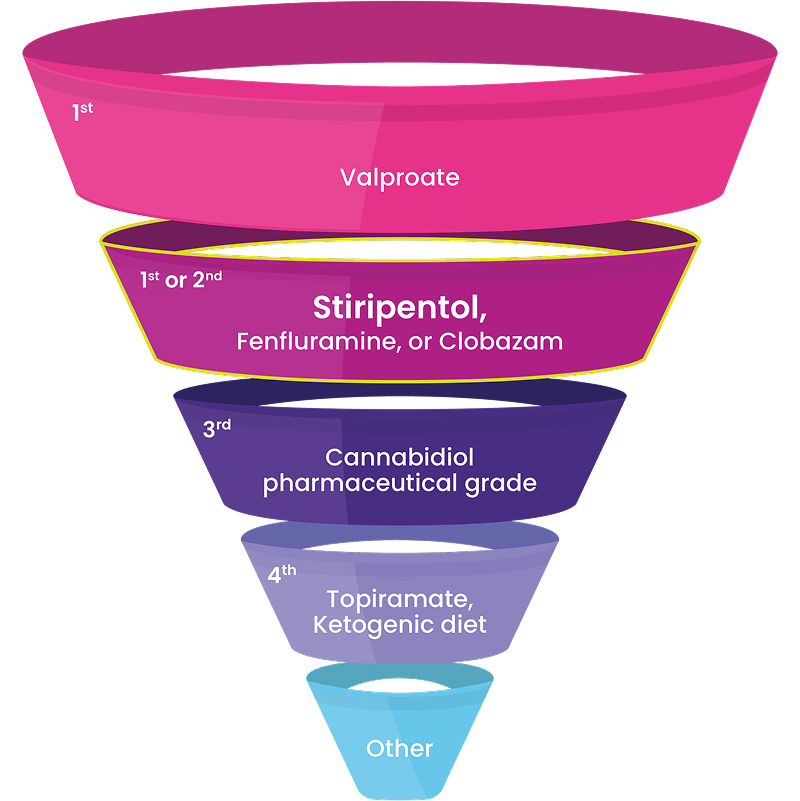
Experts Recommend DIACOMIT as First- or Second-Line Treatment4
As you navigate a new normal, know that seizure reduction and seizure freedom are possible by adding DIACOMIT to your loved one’s treatment plan.
“The demonstrated efficacy of these ‘DS-specific’ medications strongly supports their use earlier in the treatment paradigm…We should redefine our expectations of seizure control, and no longer accept seizures every 1 to 2 months as the best we can do.”4
International Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Dravet Syndrome (2022) Results with DIACOMIT may vary
It is common for patients with Dravet to be treated with multiple antiseizure medications (ASMs), including other Dravet syndrome-indicated ASMs.4
Julia, at age 7, actual patient on DIACOMITReferences
1.DIACOMIT® [prescribing information]. Beauvais, France: Biocodex, Inc.; July 2022. 2. Guerrini R, Chancharme L, Serraz B, Chiron C. Additional results from two randomized, placebo-controlled trials of stiripentol in Dravet syndrome highlight a rapid antiseizure efficacy with longer seizure-free periods. Neurol Ther. 2024;13:869-884. 3. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. CDER Clinical Review. August 2018. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2018/206709Orig1s000,207223Orig1s000MedR.pdf. Accessed May 12, 2020. 4. Wirrell EC, Hood V, Knupp KG, Meskis MA, Nabbout R, Scheffer IE, Wilmshurt J, Sullivan J. International consensus on diagnosis and management of Dravet syndrome. Epilepsia. 2022;63(7):1761-1777. 5. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Expanded access. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/public-health-focus/expanded-access. Updated March 23, 2021. Accessed July 13, 2022.